Financial Statements of Non-for-Profit Organisations
Meaning
Not-for-profit organizations also are known as non-profit organizations refer to the organizations that are set for the welfare of the society and are set-up as charitable institutions which function without any profit months. Non-profit organizations are separate legal entity not owned by any individual or enterprises. Examples, non-profit organisations are clubs, hospitals, libraries, schools, societies for promotion of sports, arts and culture etc.
- Receipts and Payments Account
The receipts and payments account is the summary of cash and bank transactions which helps in the preparation of income and expenditure account. It is prepared at the end of the accounting period and is summary of cash book, classifying receipts and payments under various heads along with cash and bank balances in the beginning and at the end of the accounting period.
Receipts are recorded on the debit side and payments are recorded on the credit side of the account. The account is maintained on cash basis of accounting.
Every receipt and payment, whether capital revenue and irrespective of the period is recorded in this account. The purpose of preparing this account is to ascertain cash in hand and cash at bank at the end of the year.
Salient Features of Receipts and Payments Account
- Nature Receipts and payments account is a real account in nature. It is basically a summary of the cash book. Cash receipts are recorded on the debit side, while cash payments are entered on the credit side.
- Period in this account, all receipts and payments irrespective of the period to which they pertain are shown.
- Capital and revenue all cash receipts and cash payments whether of capital nature or of revenue nature are included.
- Distinction No distinction is made in receipts/payments made in cash or through bank. With the exception of the opening and closing balances, the total amount of each receipt and payment is shown in this account.
- Adjustment of non-cash items Non-cash items such as depreciation, outstanding expenses, accrued income etc., are not shown in this account.
- Opening and closing balance it begins with opening balance of cash in hand and cash at bank (or bank overdraft) and close with the year-end balance of cash in hand/cash at bank (or bank overdraft). In fact, the closing balance in this account (difference between the total amount of receipts and payments) which is usually a debit balance reflects cash in hand and cash at bank unless there is a bank overdraft.
Limitations of Receipts and Payments Account
- No adjustments as the receipts and payments account is not prepared on accrual basis, therefore no adjustments are made in it.
- Does not show income and expenditure income and expenditure is not shown by this account.
- No particular accounting period Receipts and payment account does not show the amount received or paid only for a particular period.
Format of Receipts and Payments Account
Receipts and Payments Account
For the year ended..


- Income and Expenditure Account
It is the summary of income and expenditure for the accounting year. Income and expenditure account in nominal account in nature and serves the same purpose and the profit and loss account of a business organisation does. Income and expenditure account is prepared at the end of accounting period to ascertain net operating results. All the revenue items relating to the current period are shown in this account, the expenditure and losses on the expenditure side and incomes and gains on the income side of the account. It shows the operating results in the form of surplus (i.e. excess of income over expenditure) or deficit (i.e. excess expenditure over income) which is transferred to the capital fund shown in the balance sheet. The income and expenditure account is prepared on the accrual basis.
Features of Income and Expenditure Account
- Nature it is a nominal account.
- No capital items No capital items are entered in this account.
- Debit and credit sides its debit side includes all the expenses pertaining to the particular period and certain side includes all the incomes pertaining to the same period.
- Opening and closing balances no opening and closing balances are recorded in it.
- Only current period items No item either revenue or expenditure, pertaining to the past period or the future period is entered in this account.
- Similar to profit and loss account this account is prepared in the same manner in which a profit and loss account is prepared.
- Surplus/Deficit Credit balance is called ‘excess of income over expenditure’, i.e. surplus and debit balance is called ‘excess of expenditure over income’, i.e. deficit.
The format of Income and Expenditure Account
Income and Expenditure Account
For the year ended..

- Either of the two will appear.
- Balance Sheet
Balance Sheet is prepared by not-for-profit organisation to ascertain the financial position of the organisation. It is prepared on the same pattern as that of the business entities. Balance sheet is prepared at the end of the accounting period after preparing income and expenditure account.
Sometimes, balance sheet needs to be prepared at the beginning of the year in order to find out the opening balance of the capital/general fund. The balance sheet shows assets on the right hand side and liabilities are shown on the left hand side along with capital fund or gener.al fund.
The capital fund or general fund is in place of the capital and the surplus or deficit as per incomes and expenditure account shall be added to/deducted from this fund.
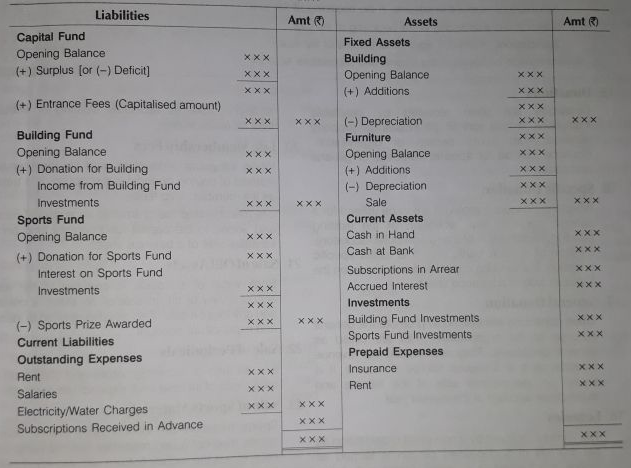
- Format of Balance Sheet
Balance Sheet
As at..
- Fund Based Accounting
The accounting where receipts and incomes relating to a particular fund are credited to that particular fund and payments and expenses are debited to that particular fund, it is known as fund based accounting.
These funds are created for specific purposes, e.g. prize fund, sports fund, library fund, building fund, endowment fund etc. If the fund account has a credit balance, it is shown in the balance sheet on the liabilities side. If the fund account has a debit balance, i.e. the fund is less than the balance, it is transferred to the debit of income and expenditure account.
- Classification of Funds
Funds may be classified as
- Unrestricted Funds
- Restricted Funds
Various types of restricted funds are as follows:
- Endowment fund
- Annuity fund
- Loan fund
- Fixed assets fund
- Prize fund
Subscriptions
It is the membership fee paid by the members on annual basis. It is the main source of income of non-prime organisations. Subscriptions relating to the current year whether received or not, are shown in the credit side and income and expenditure account. Subscriptions not received, i.e. outstanding are shown on the assets side and balance sheet. Subscriptions received in advanced for the following year are shown on the liabilities side in the balance sheet.
Table Showing Calculation of Subscriptions

Donation
Donations are often received by charitable institutions. It is a sort of gift in cash or properly received from some person or organisation. Donation can be for specific purposes or general purposes.
Specific Donation
When the donations received are to be utilized for a specific purpose say, extension of the existing building, construction of a new computer laboratory, creation of a book bank, etc. it is called specific donation. It should be capitalized and shown on the liabilities side of a balance sheet.
General Donation
When donations are utilized to promote the general purpose of the organisation, they are called as general donations. They are treated as revenue receipts, as it is a regular source of income. It is shown on the income side of the income and expenditure account of the current year.
Legacies
The amount received by a non-profit organisation as per the will of a deceased person is termed as legacy. It is treated as a capital receipt and shown on the liabilities side. However, legacies of small amount may be treated as income and shown on the income side of the income and expenditure account.
Entrance Fees
Entrance fee also known as admission fee is paid only once by the member at the time of becoming a member. As entrance fee is paid by a member only once, it is argued that it should be treated as a capital receipt and transferred to capital fund. However, it should be treated as revenue receipt and credited to the income and expenditure account, when the amount is small to cover the expenses of admission. NCERT guidelines advocate treating of entrance fees as revenue item.
Life Membership Fees
When lump sum amount is paid by the member instead of paying periodic, subscription, it is treated as life member-ship fees.
Life membership fee is treated as a capital received and added to the capital fund/general fund on the liabilities side of a balance sheet.
- Sale of Old Assets
Book value of an asset is credited to the asset account. Any profit on sale of an asset is credited and loss on sale of an asset is debited to income and expenditure account.
Sale of Periodicals
It is an item of recurring nature and shown in the credit side of income and expenditure account.
Sale of Sports Material
Sports materials are consumable assets. Sales sports material (used material like old balls, bills net etc.) is the regular feature with any sport club is usually shown as an income in the income and expenditure account.
Payment of Honorarium
Honorarium is the amount paid to the person who is not an employee of the institution and has voluntary undertaken a service. It is debited to income and expenditure account.
Endowment Fund
It is a fund arising from a bequest or gift, the income of which is devoted for a specific purpose. Hence, it is a capital receipt and shown on the liabilities of the balance sheet as an item of a spend purpose fund.
Government Grants
Various institutions like schools. Colleges, public hospitals etc., depend on government grants for their activities. Grants which are recurring in nature are treated as revenue receipt and credited to income and expenditure account. However, grants of capital nature such as building grant are treated as capital receipt and transferred to building account.
Special Funds
Certain special funds are created for certain purpose/activities, e.g. prize funds, match, fund, sports fund, etc. The income earned from such funds is added to the respective fund and not credited to income and expenditure account and also the expenses incurred on such specific purposes are also deducted from the special fund.
Special Receipts
When there is a receipt of amount by non-profit organisations for special occasions, it is referred to as special receipts. Such amounts are credited to a separate account and expenses against these receipts are debited to it. The balance is transferred to the credit side of income and expenditure account.
Sale of Old Newspapers
Amount which is realized by selling of old newspapers is treated as income and credited to income and expenditure account.
Revenue Receipts
Revenue receipts are shown on the credit side of income and expenditure account, e.g. rent, interest on investment, proceeds from concerts, shows, etc.
Revenue Expenses
Revenue expenses are the expenses which are incurred for performing day-to-day activities or expenses which are recurring in nature, e.g. salary, rent, etc. It also includes expenses incurred on the maintenance of fixed assets, e.g. repairs, depreciation etc.
Capital Expenditure
Capital expenditures are shown on the assets side of balance sheet, e.g. expenditure on purchases of books, furniture, medicines, postage, etc.
Calculation of the Cost of Consumable Goods
Consumable goods are the items which are consumed during the year such as stationery, sports material, foodstuff, medicines, postage etc.
Non-Profit organisations have stock of consumable goods at the end of the year. The income and expenditure account will show correct surplus/deficit, only if the goods consumed are debited to income and expenditure account and closing stock is shown in the balance sheet.
The amount of goods consumed during the year is calculated as follows:

- Preparation of the Income and Expenditure Account and the Balance Sheet from the Receipts and Payments Account with the Additional Information
Step 1 Prepare the opening balance sheet to find out the opening balance of capital fund (in case it is not given), taking into account the opening cash and bank balances given in receipts and payments account and other assets and liabilities given in additional information. The difference between the assets and liabilities is the capital fund or general fund or accumulated fund.
Step 2Identify from the receipts side, i.e. debit side of the receipts and payments account, the revenue receipts and the capital receipts.
- Capital receipts are shown in the appropriate assets and liabilities account and then incorporated in the balance sheet.
- Record the revenue receipts on the income side, i.e. credit side of income and expenditure account, after making suitable adjustments so that all revenue receipts for the current year are shown.
Step 3From the receipts and payments account, identify the revenue and capital payments from the payments side, i.e. credit side.
- Capital payments are shown in the appropriate assets and liabilities account and then incorporated in the balance sheet.
- Record the revenue payments on the expenditure side, i.e. debit side of the income and expenditure account, for the current year after making necessary adjustments.
Step 4There are certain items which do not appear in receipts and payments account but are to be recorded in income and expenditure account. They are depreciation on fixed assets- it is to be shown on the debit side, loss on sale of fixed assets- to be shown on the debit side, profit on sale of fixed assets-to be shown on the credit side.
Step 5 Surplus/Deficit in the income and expenditure account is calculated and transferred to the capital fund shown in the balance sheet. Excess of incomes over expenditure is surplus and excess of expenditure over incomes is deficit.
Step 6 Prepare closing balance sheet by taking into consideration the opening balance of assets, liabilities and opening capital fund, surplus/deficit, purchase and sale of assets during the year.