A hyperbola is the locus of a point in a plane which moves in the plane in such a way that the ratio of its distance from a fixed point in the same plane to its distance from a fixed line is always constant, which is always greater than unity.
The fixed point is called the focus and the fixed line is directrix and the ratio is the eccentricity.
Transverse and Conjugate Axes
The line through the foci of the hyperbola is called its transverse axis.
The line through the centre and perpendicular to the transverse axis of the hyperbola is called its conjugate axis.
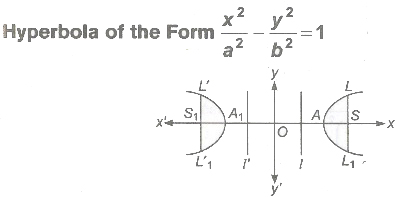
- Centre O(0, 0)
- Foci are S(ae,0),S1(-ae, 0)
- Vertices A(a, 0), A1(-a, 0)
- Directrices / : x = a/e, l’ : x = -a/e
- Length of latusrectum LL1 = L’L’1 = 2b2/a
- Length of transverse axis 2a.
- Length of conjugate axis 2b.
- Eccentricity
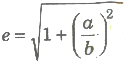 or b2 = a2(e2 – 1)
or b2 = a2(e2 – 1) - Distance between foci =2ae
- Distance between directrices = 2a/e
Conjugate Hyperbola
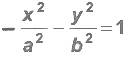
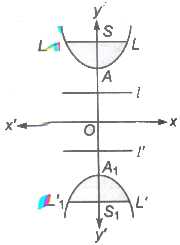
- (i) Centre O(0, 0)
- (ii) Foci are S (0, be), S1(0, — be)
- (iii) Vertices A(0, b) , A1(0, — b)
- (iv) Directrices
l:y = b/e, l’ : y = —b/e - (v) Length of latusrectum
LL1 = L’ L’1 = 2a2/b - (vi) Length of transverse axis 2b.
- (vii) Length of conjugate axis 2a.
- (viii) Eccentricity
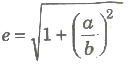
- (ix) Distance between foci = 2be
- (x) Distance between directrices = 2b/e
Focal Distance of a Point
The distance of a point on the hyperbola from the focus is called it focal distance. The difference of the focal distance of any point on a, hyperbola is constant and is equal to the length of transverse axis the hyperbola i.e.,
S1P — SP = 2a
where, S and S1 are the foci and P is any point or P the hyperbola.
Equation of Hyperbola in Different Form
1 If the centre of the hyperbola is (h, k) and the directions of the axes are parallel to the coordinate axes, then the equation of the hyperbola, whose transverse and conjugate axes are 2a and 2b is
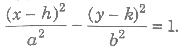
2. If a point P(x, y) moves in the plane of two perpendicular straight lines a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and b1x – a1y + c2 = 0 in such a way that
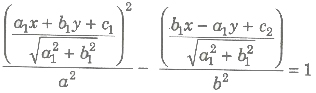
Then, the locus of P is hyperbola whose transverse axis lies along b1x – a1y + c2 = 0 and conjugate axis along the line a1x + b1y + c1 = 0. The length of transverse and conjugate axes are 2a and 2b, respectively.
Parametric Equations
(i) Parametric equations of the hyperbola![]()
x = a sec θ, y = b tan θ
or x = a cosh θ, y = b sinhθ
(ii) The equations![]() are also the parametric equations of the hyperbola.
are also the parametric equations of the hyperbola.
Equation of Chord
(i) Equations of chord joining two points P(a sec θ1, b tan θ1,) and Q(a sec θ2, b tan θ2) on the hyperbola
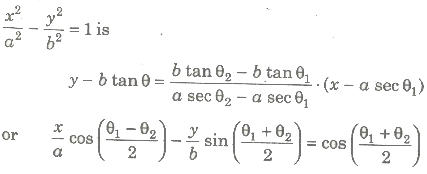
(ii) Equations of chord of contact of tangents drawn from a point (x1, y1) to the hyperbola![]()
(iii) The equation of the chord of the hyperbola![]() bisected at point (x1, y1) is given by
bisected at point (x1, y1) is given by
![]()
Equation of Tangent Hyperbola
(i) Point Form The equation of the tangent to the hyperbola ![]()
(ii) Parametric Form The equation of the tangent to the hyperbola![]()
(iii) Slope Form The equation of the tangents of slope m to the hyperbola![]()
The coordinates of the point of contact are
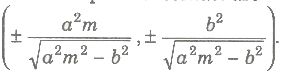
(iv) The tangent at the points P(a sec θ1 , b tan θ1) and Q (a sec θ2, b tan θ2) intersect at the point
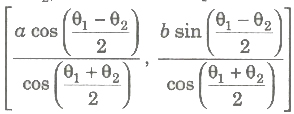
(v) Two tangents drawn from P are real and distinct, coincident or imaginary according as the roots of the equation m2(h2 – a2) – 2khm + k2 + b2 = 0. are real and distinct, coincident or imaginary.
(vi) The line y = mx + c touches the hyperbola, if c2 = a2m2 – b2 the point of contacts![]()
Normal Equation of Hyperbola
(i) Point Form The equation of the normal to the hyperbola![]()
(ii) Parametric Form The equation of the normal at (a sec θ, b tan θ) to the hyperbola![]()
is ax cos θ + by cot θ = a2 + b2.
(iii) Slope Form The equations of the normal of slope m to the hyperbola![]() are given by
are given by
![]()
The coordinates of the point of contact are
![]()
(iv) The line y = mx + c will be normal to the hyperbola![]() if,
if,
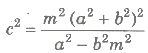
(v) Maximum four normals can be drawn from a point (x1, y1) to the hyperbola![]()
Conormal Points
Points on the hyperbola, the normals at which passes through a given point are called conormal points.
- The sum of the eccentric angles of conormal points is an odd ion multiple of π.
- If θ1 , θ2 , θ3 and θ4 are eccentric angles of four points on the hyperbola
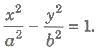 , then normal at which they are concurrent, then
, then normal at which they are concurrent, then
(a) ∑cos( θ1 + θ2) = 0
(b) ∑sin( θ1 + θ2) = 0 - If θ1 , θ2 and θ3 are the eccentric angles of three points on the hyperbola
 , such that sin(θ1 + θ2) + sin(θ2 + θ3) + sin(θ3 + θ1) = 0. Then, the normals at these points are concurrent.
, such that sin(θ1 + θ2) + sin(θ2 + θ3) + sin(θ3 + θ1) = 0. Then, the normals at these points are concurrent. - If the normals at four points P(x1, y1), Q(x2, y2), R(x3 , y3) and S(X4, y4) on the hyperbola
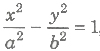 are concurrent, then
are concurrent, then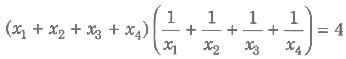
Conjugate Points and Conjugate Lines
- Two points are said to be conjugate points with respect to a hyperbola, if each lies on the polar of the other.
- Two lines are said to be conjugate lines with respect to a hyperbola
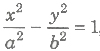 , if each passes through the pole of the other.
, if each passes through the pole of the other.
Diameter and Conjugate Diameter
- Diameter The locus of the mid-points of a system of parallel chords of a hyperbola is called a diameter.>
The equation of the diameter bisecting a system of parallel chord of slope m to the hyperbola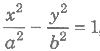 is
is
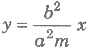
- Conjugate Diameter The diameters of a hyperbola are sal to be conjugate diameter, if each bisect the chords parallel to th other.
The diameters y = m1x and y = m2x are conjugate, if m1 m2 = b2/a2. - In a pair of conjugate diameters of a hyperbola, only one mee the hyperbola in real points.
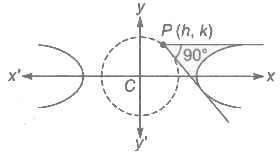
Asymptote
An asymptote to a curve is a straight line, at a finite distance from the origin, to which the tangent to a curve tends as the point of contact goes to infinity.
- The equation of two asymptotes of the hyperbola
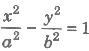 are
are 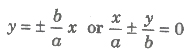
- The combined equation of the asymptotes to the hyperbola
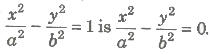
- When b = a, i.e., the asymptotes of rectangular hyperbola x2 – y2 = a2 are y = ± x which are at right angle.
- A hyperbola and its conjugate hyperbola have the same asymptotes.
- The equation of the pair of asymptotes differ the hyperbola and the conjugate hyperbola by the same constant only i.e., Hyperbola — Asymptotes = Asymptotes — Conjugate hyperbola
- The asymptotes pass through the centre of the hyperbola.
- The bisectors of angle between the asymptotes are the coordinate axes.
- The angle between the asymptotes of
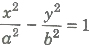 is 2 tan-1(b/a) or 2 sec-1(e).
is 2 tan-1(b/a) or 2 sec-1(e).
Director Circle
The locus of the point of intersection of the tangents to the hyperbolo![]() , which are perpendicular to each other, is called a director circle. The equation of director circle is x2 + y2 = a2 – b2.
, which are perpendicular to each other, is called a director circle. The equation of director circle is x2 + y2 = a2 – b2.
Rectangular Hyperbola
A hyperbola whose asymptotes include a right angle is said to I rectangular hyperbola or we can say that, if the lengths of transver: and conjugate axes of any hyperbola be equal, then it is said to be rectangular hyperbola.
i.e., In a hyperbola![]() . if b = a, then it said to be rectangular hyperbola.
. if b = a, then it said to be rectangular hyperbola.
The eccentricity of a rectangular hyperbola is always √2.
Rectangular Hyperbola of the Form x2 – y2 = a2
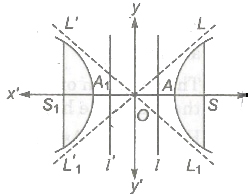
- Asymptotes are perpendicular lines i.e., x ± y = 0
- Eccentricity e = √2.
- Centre (0, 0)
- Foci (± -√2 a, 0)
- Vertices A(a, 0) and A1 (—a, 0)
- Directrices x = + a/√2
- Latusrectum = 2a
- Parametric form x = a sec θ, y = a tan θ
- Equation of tangent, x sec θ – y tan θ = a
Rectangular Hyperbola of the Form xy = c2
- Asymptotes are perpendicular lines i.e., x = 0 and y = 0
- Eccentricity e = √2
- Centre (0, 0)
- Foci S(√2c, √2c), S1(-√2c, -√2c)
- Vertices A(c, c), A1(— c,— c)
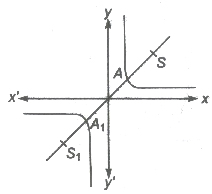
- Directrices x + y = ±√2c
- Latusrectum = 2√2c
- Parametric form x = ct, y = c/t
Tangent Equation of Rectangular Hyperbola xy = c2
- Point Form The equation of tangent at (x1, y1) to the rectangular hyperbola is xy1 + yx1= 2c2 or (x/x1 + y/y1) = 2.
- Parametric Form The equation of tangent at (ct, c/t) to the hyperbola is( x/t + yt) = 2c.
- Tangent at P(ct1, c/t1) and Q (ct2, c/t2) to the rectangular hyperbola intersect a
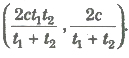
- The equation of the chord of contact of tangents drawn from a point (x1, y1) to the rectangular hyperbola is xy1 + yx1 = 2c2.
Normal Equation of Rectangular Hyperbola xy = c2
- Point Form The equation of the normal at (x1, y1) to the rectangular hyperbola is xx1 – yy1 = x12 – y12.
- Parametric Form The equation of the normal at ( ct, c/t)to the rectangular hyperbola xy = c2 is xt3 — yt — ct4 + c = O.
- The equation of the normal at( ct, c/t)is a fourth degree equation t in t. So, in general four normals can be drawn from a point to the hyperbola xy = c2.
Important Points to be Remembered
- The point (x1, y1) lies outside, on or inside the hyperbola
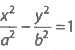 according as
according as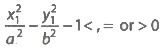
- The combined equation of the pairs of tangent drawn from a point P(x1, y1) lying outside the hyperbola
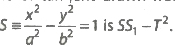
- The equation of the chord of the hyperbola xy = c2 whose mid-point is (x1, y1) is
xy1 + yx1 = 2x1y1
or t = S1 - Equation of the chord joining t1, t2 on xy = t2 is
x + yt1t2 = c(t1 + t2) - Eccentricity of the rectangular hyperbola is √2 and the angle between asymptotes is 90°.
- If a triangle is inscribed in a rectangular hyperbola, then its orthocentre lies on the hyperbola.
- Any straight line parallel to an asymptotes of a hyperbola intersects the