UNIT X: BALANCE OF PAYMENTS AND FOREIGN EXCHANGE RATE
Foreign Exchange refers to all currencies other than the domestic currency of a given country.
Foreign exchange rate is the rate at which currency of one country can be exchanged for currency of another country.
Foreign Exchange Market: The Foreign Exchange market is the market where the national currencies are traded for one another.
Functions of Foreign Exchange Market:
- Transfer function: It transfers the purchasing power between countries.
- Credit function: It provides credit channels for foreign trade
- Hedging function: It protects against foreign exchange risks.
FIXED EXCHANGE RATE SYSTEM: Fixed exchange rate is the rate which is officially fixed by the government, monetary authority and not determined by market forces.
FLEXIBLE EXCHANGE RATE: Flexible exchange rate is the rate which is determined by forces of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market.
DEMAND FOR AND SUPPLY OF FOR FOREIGN EXCHANGE
Demand for foreign exchange:
- To purchase goods and services from other countries
- To send gifts abroad
- To purchase financial assets (shares and bonds)
- To speculate on the value of foreign currencies
- To undertake foreign tours
- To invest directly in shops, factories, buildings
- To make payments of international trade.
Supply of foreign exchange:
Foreign currencies flow into the domestic economy due to the following reason.
- When foreigners purchase home countries goods and services through exports
- When foreigners invest in bonds and equity shares of the home country.
- Foreign currencies flow into the economy due to currency dealers and speculators.
- When foreign tourists come to India
- When Indian workers working abroad send their saving to families in India.
EQUILIBRIUM IN THE FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKET
The equilibrium exchange rate is determined at a point where demand for and supply of foreign exchange are equal. Graphically interaction of demand and supply curve determines the equilibrium exchange rate of foreign currency.
y
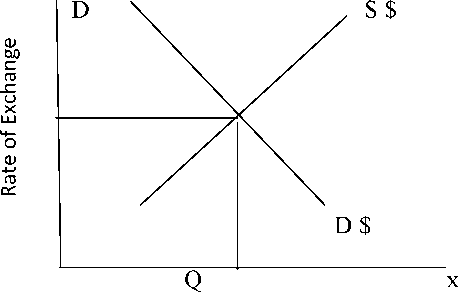
Demand and supply of US$
Managed Floating: This is the combination of fixed and flexible exchange rate. Under this, country manipulates the exchange rate to adjust the deficit in the B.O.P by following certain guidelines issued by I.M.F.
Dirty floating: If the countries manipulate the exchange rate without following the guidelines issued by the I.M.F is called as dirty floating.
BALANCE OF PAYMENTS: MEANING AND COMPONENTS
Meaning: The balance of payments of a country is a systematic record of all economic transactions between residents of a country and residents of foreign countries during a given period of time.
BALANCE OF TRADE AND BALANCE OF PAYMENTS
Balance of trade: Balance of trade is the difference between the money value of exports and imports of material goods (visible item)
Balance of payments: Balance of payments is a systematic record of all economic transactions between residents of a country and the residents of foreign countries during a given period of time. It includes both visible and invisible items. Hence the balance of payments represents a better picture of a country’s economic transactions with the rest of the world than the balance of trade.
STRUCTURE OF BALANCE OF PAYMENT ACCOUNTING
A balance of payments statement is a summary of a Nation’s total economic transaction undertaken on international account. There are two types of account.
1. Current Account: It records the following 03 items.
- Visible items of trade: The balance of exports and imports of goods is called the balance of visible trade.
- Invisible trade: The balance of exports and imports of services is called the balance of invisible trade E.g. Shipping insurance etc.
- Unilateral transfers: Unilateral transfers are receipts which resident of a country receive (or) payments that the residents of a country make without getting anything in return e.g. gifts.
The net value of balances of visible trade and of invisible trade and of unilateral transfers is the balance on current account.
- CAPITAL ACCOUNT: It records all international transactions that involve a resident of the domestic country changing his assets with a foreign resident or his liabilities to a foreign resident.
VARIOUS FORMS OF CAPITAL ACCOUNT TRANSACTIONS
- Private transactions: These are transactions that are affecting assets (or) liabilities by individuals.
- Official transactions: Transactions affecting assets and liabilities by the government and its agencies.
- Direct Investment: It is the act of purchasing an asset and at the same time acquiring and control of it.
- Portfolio investment: It is the acquisition of assets that does not give the particular control over the asset.
The net value of balances of direct and portfolio investment is called the balance on capital account.
OTHER ITEMS IN THE BALANCE OF PAYMENT
They are included since the full balance of payments account must balance. These items are as follows.
- Errors and Omissions: They may arise due to the presence of sampling and due to his honesty.
- Official reserve transactions: All transactions except those in this category may be termed as autonomous transactions. They are so called because they were entered into with some independent motive. Balance of payments always balance.
AUTONOMOUS AND ACCOMMODATING ITEMS
Autonomous items: Autonomous items in the B.O.P refer to international economic transactions that take place due to some economic motive such as profit maximization. These items are often called above the line items in the B.O.P.
The balance of payments is in a deficit if the autonomous receipts are less than autonomous payments. The monetary authorities may finance a deficit by depleting their reserves of foreign currencies, or by borrowing from I.M.F.
Accommodating items: Accommodating items in the B.O.P. refer to transactions that occur because of other activity with the B.O.P such as government financing. Accommodating items are also referred to as below the line of items.
DISEQUILIBRIUM THE BALANCE OF PAYMENTS
There are a number of factors that cause disequilibrium in the balance of payments showing either a surplus or deficit. These causes are categorized into 3 factors.
- Economic factors: Large scale development expenditure that may cause large imports.
Cyclical fluctuations in general business activities such as recession or depression.
High domestic prices may result in imports.
- Political factors: Political instability may cause large capital outflows and hamper the inflows of foreign capital.
- Social factors: Changes in tastes, preferences and fashions may affect imports and exports.
Ans: Foreign exchange rate is the rate at which currency of one country can be exchanged for currency of another country.
Ans: The foreign exchange market is the market where international currencies are traded for one another.
Ans: Fixed Rate of exchange is a rate that is fixed and determined by the government of a country and only the government can change it.
Ans: Equilibrium exchange rate occurs when supply of and demand for foreign exchange are equal to each other.
Ans: Flexible rate of exchange is that rate which is determined by the demand and supply of different currencies in the foreign exchange market.
Ans: Appreciation of a currency occurs when its exchange value in relation to currencies of other country increases.
Ans: The spot exchange rate refers to the rate at which foreign currencies are available on the sport.
Ans: Market for foreign exchange for future delivery is known as the forward market.
Ans: Balance of payments refers to the statement of accounts recording all economic transactions of a given country with the rest of the world.
Ans: Balance of trade is the difference between the value of imports and exports of only physical goods.
- The balance of trade shows a deficit of Rs. 600 crores, the value of exports is Rs.1000 crores. What is value of Imports?
Ans: Balance of Trade = Exports of goods – import of goods
Import of good = Export of goods – (B.O.T)
= 1000- (-600)
= Rs. 1600.
Ans: – Balance of trade
Ans:- Disequilibrium in BOP is means either there is a surplus or deficit in balance of payment account.
Ans:- i) external assistance ii) commercial borrowing iii) foreign investment
Ans:- Accommodating transactions bring balance in the BOP account.
Ans:- Autonomous items in BOP refers to international economic transaction that take place due to some economic motive such as profit maximization. These items are independent of the state of the country balance of payments.
Ans:- The other name of autonomous items in BOP is above the line item.
Ans:- A situation of deficit in BOP arise when autonomous receipts are less than autonomous payments.
Ans:- It is a system that allows adjustments in exchange rate according to a set of rules and regulations which are officially declared in the foreign exchange market.
Ans:- Manipulate the exchange rate without following the guidelines issued by IMF is called dirty floating.
ANSWER QUESTIONS (3 / 4 MARKS)
Ans:- Foreign exchange is demanded for the following purposes.
- Payment of International loans
- Gifts and grants to rest of the world
- Investment in rest of the world.
- Direct purchases abroad for goods and services as well as imports from rest of the world.
- What determines the flow of foreign exchange in to the country?
Ans: – Following factors contribute to the flow of foreign exchange in to the country.
- Purchases of domestic goods by the foreigners
- Direct foreign investment and portfolio investment in the home country.
- Speculative purchase of foreign exchange.
- When foreign tourists come to India.
- Why does the demand for foreign exchange rise, when it price falls?
Ans:- With a fall in price of foreign exchange , the exchange value of domestic currency increases and that of foreign currency falls. This implies that foreign goods become cheaper and their domestic demand increases. The rising domestic demand for foreign goods implies higher demand for foreign exchange. So there is inverse relationship between price and demand for foreign exchange.
Ans: When price of a foreign currency falls it makes exports, investment by foreign residents costlier as a result supply of foreign currency falls.
Ans: Autonomous transactions are done for some economic consideration such as profit, such transactions are independent of the state of B.O.P. Accommodating transactions are under taken to cover the deficit/surplus in balance of payments.
price
Ans:
Give two examples explain why there is a rise in demand for a foreign currency when its
|
Sl. |
Forms of |
Very Short (1 |
Short Answer |
Long |
Total |
|
1 |
Unit 1 |
1(1) |
3(1) |
— |
4 |
|
2 |
Unit 2 |
1(2) |
3(2), 4(1) |
6(1) |
18 |
|
3 |
Unit 3 |
3(1) |
3(1), 4(2) |
6(1) |
18 |
|
4 |
Unit 4 |
1(1) |
3(1) |
6(1) |
10 |
|
5 |
Unit 5 |
Not to be tested |
|||
|
6 |
Unit 6 |
— |
3(3) |
6(1) |
15 |
|
7 |
Unit 7 |
1(2) |
— |
6(1) |
08 |
|
8 |
Unit 8 |
1(2) |
4(1) |
6(1) |
12 |
|
9 |
Unit 9 |
— |
4(2) |
— |
08 |
|
10 |
Unit 10 |
1(1) |
3(2) |
— |
07 |
|
Sub Total |
10(10) |
30(10), 24(6) |
36(6) |
100 |
|
When price of foreign currency falls, imports are cheaper. So, more demand for foreign exchange by importers.
falls.
Tourism abroad is promoted as it becomes cheaper. So demand for foreign currency rises.
Distinguish between fixed and flexible foreign exchange rate.
Ans: When foreign exchange rate is fixed by Central Bank/government, it is called fixed exchange rate. When foreign exchange rate is determined by market forces/mechanism, it is flexible exchange rate.