UNIT 7
Directing as a function of managment, refers to the process of instructing, guiding counselling, motivating and leading people in the organisation to achieve its objectives. It does not mean only instructions but also include supervising the employess when they are performing the job, motivating them to perform more efficiently and leading them towards the achievement of organisational goal.
- Directing initiate action : The other functions of management prepare a setting for action, but directing initiates action in the organisation.
- Directing takes place at every level of Management :- Every manager from top executive to supervisor performs the function of directing.
- Directing is a continous process of supervision, communication, leadership and motivation, It takes place throughout the life of the organisation.
- Directing flows from top to bottom :- It is first initiated at the top level and flows to the bottom through organisational hierarchy.
- Initiates Action : It helps to initiate action by people in the organisation towards attainment of desired objectives. The employees start working only when they get instructions and directions from their superiors. It is the directing function which starts actual work to convert plans into results.
- Integrate Employee s Efforts :- All the activities of the oranisation are interrelated so it in necessary to coordinate all the activities. It integrates the activities of subordinates by supervision, guidance and counselling.
|
3. |
Means of motivation – It motivates the subordinates to work efficiently and to contribute their maximum efforts towards the achievement of organisational goals. |
|
4. |
Facilitates change :- Employees often resist changes due to fear of adverse effects on their employment and promotion. Directing facilitate adjustment in the organisation to cope with changes in the environment. |
|
5. |
Stability and Balance in the organisation :- It helps to achieve balance between individual interests of employees and organisational interests. |
|
Principles of Directing |
|
|
1. |
Maximum Individual Contribution : – Directing techniques must help every individual in the organisation to contribute his maximum potential for achievement of organisational objectives. |
|
2. |
Harmony of objectives – The objectives of individual and organisation must be in harmony with each other. But good directing should provide harmony by convincing the employees that organisational objectives are in their own interest. |
|
3. |
Unity of Command :- An individual or subordinate in the organisation should receive instructions from one superior only otherwise it creates confusion conflict and disorder in the organisation. |
|
4. |
Appropriateness of Direction Technique : According to this principle the technique like motivation, supervision, communication and leadership should be appropriate – according to the attitude and need of the employees. |
|
5. |
Managerial Communication : The two way flow of information is the most effective means of securing cooperation of the subordinates because it provides them an opportunity to express their feelings. |
|
6. |
Use of Informal organisation :- An informal organisation exist within formal organisation structure. So managers must make use of informal structure also for getting correct and real feed back. |
|
7. |
Leadership – A manager by becoming a good leader can make direction effective with the trust and confidence of his subordinates. |
|
8. |
Follow through : Mere giving of an order is not sufficient managers should follow it up by reviewing continuously. |
|
47 XII – Business Studies |
|

1. Supervision – It means observing the subordinates at work to see that they are working in according with plans and to help them in solving their problems. The important thing in supervision is it involves face to face contact between superior and subordinates. Supervisor s position is immediately above the worker.
Importance of Supervision / Role of a Supervisor
- Link between workers and management because the supervisor explains management policies to worker and brings workers problems to the notice of the management.
- Ensures issuing Instructions : To make sure that the instructions are communicated to each and every employee.
- Facilities Control : – Control means match between actual and planned output. It ensures checking on the methods in use and progress of work according to planned schedule.
- Maintainence of Discipline : The strict supervision and guidance of supervisor encourages the employees and workers to be more disciplined in the activities.
- Feedback – The supervisors are directly dealing with the subordinates, As a result feedback in the form of suggestions, grievances keeps coming to the management.
- Improved Motivation – A supervisor with good leadership qualities can build up high morale among workers.
- Optimum utilisation of resources All the activities are under the observation of supervisor so less wastages and optimum utilisation of resources is possible.
Meaning :- It is the process of stimulating people to act to their best ability
to accomplish desired goals. It depends upon satisfying needs of people.
- Psychological phonomenon – It is personal and internal feelings which arises from the needs and wants of a person.
- Goal Directed Behaviour – It includes people to behave in such a manner so that they can achieve their goal.
- Motivation can be either positive or Negative – Positive motivation means inspiring people to work better and appreciating a work that is well done. Negative motivation means forcing people to work by threatening or punishing them.
- Complex Process :- It is a complex and difficult process. Individuals differ in their needs and wants and moreover human needs change from time to time.
Motivation Process –
It is based on human needs.
Unsatisfied Needs
Tension
Drives
Search Behaviour
Satisfied Need
Reduction of Tension
An Unsatisfied needs of an individual creates tension which stimulates his or her drives. These drives generate a search behaviour to satisfy such need. If such need is satisfied, the individual is relieved of tension.
- Achievement of Organisational Goal : Motivation puts human resources into action by satisfying their needs through appropriate rewards. Motivated employees cooperate and contribute their maximum efforts towards the organisational goals.
- Higher Efficiency of Employees – Depends upon their abilities and willingness to work hard. It bridges the gap between the ability to work and willingness to work and willingness always improves efficiency.
- Reduction in resistance to change It helps to overcome resistance to change.
- Stability in workforce – It brings confidence in employees and also improve their loyality and commitment towards the organisation. As a result the rates of labour absenteeism and labour turnover reduce.
- Optimum Utilisation of Resources – The motivated workers would handle machines and materials properly. This would ensure optimum utilisation of resources and reduction of wastage.
Financial and Non-Financial Incentives – Incentive means all measures which are used to motivate people to improve performance.
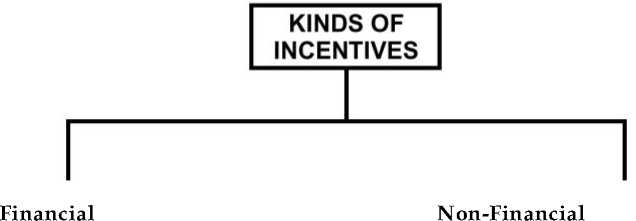
Profit sharing
Pay and Allowances
Bonus
Retirement Benefits Perquisites
Productivity linked wage in centuries
Co-partnership/stock option
Status
Career Advancement
Opportunity
Job enrichment
Employee Recognition programmer
Employees participation Job security
Employees empowerment
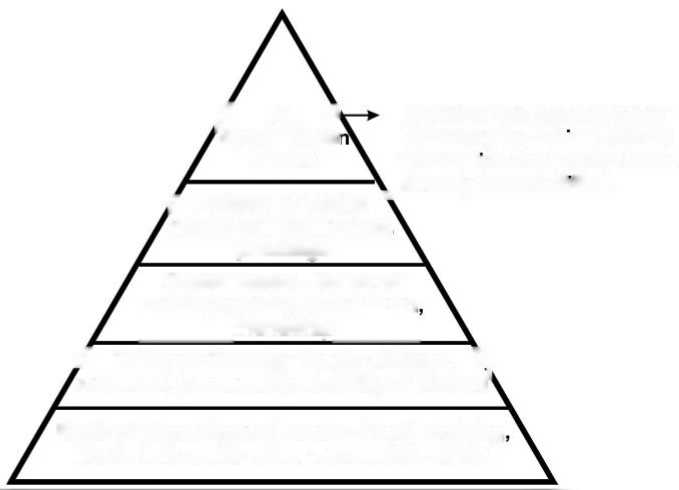
Maslow s Need Hierarchy Theory of Motivation :- Maslow s Theory focuses on the needs as the basis for motivation
Example from the point
view of Individual
Example from the point of view of organisation
Self fulfilments
Achievement of goals
Status
Jobtitle
Friendship
Cordial relation with collegues
Stability of Income
Pension Plan
Hunger
Basic Salary
f Self J
rActualisatioi
Needs
Needs of the highest order
Generally found in persons
whose first four needs have
f Esteem or Status ‘
needs self confidence,
prestidge
already been fulfilled.
Social Needs – Sense of Belongingness, association friendship
/ Safety or Security Needs – Oldage, \ sickness, job security, stability of income’
Basic of physiclogical needs – Food, clothing
Shelter, air, water, other necessities of life.
Leadership is the activity of influencing people to strive willingly for mutual objectives. Managers at all levels are expected to the leaders of their subordinates.
- Influence behaviour : It indicates ability of an individual to influence others.
- Interpersonal relations : It tries to bring change in the behaviour of others.
|
3. |
Common goals : It is exercised to achieve common goals of the organisation. |
|
4. |
Contnuous process : It is a continous process. |
|
5. |
Situational : There a no particular style of leadership it is related to particular situation. |
|
Importance :- 1. Help in guiding and inspiring employees. |
|
|
2. |
Creates confidence – by recognising the Quality and capabilities of individuals. |
|
3. |
Handles conflicts effectively and does not allow adverse effects resulting from the conflics. |
|
4. |
Provides Training to Subordinates . |
|
5. |
Secures cooperation of members of organisation |
|
6. |
Inspires productivity |
|
7. |
Improves job satisfaction |
|
8. |
Achievement of organisational goals |
|
9. |
Introducing required changes. |
|
Qualities of a Good Leader |
|
|
1. |
Physical Features – Health and endurance help a leader to work hard which inspires others also to work with same spirit. |
|
2. |
Knowledge – A leader must be able to examine every problem in the right direction. |
|
3. |
Integrity – He should be a model to others regarding his ethics and values. |
|
4. |
Initiative – He should not wait for opportunities come to his way rather he should grab the opportunities. |
|
5. |
Motivation skills – To understand the needs of people and motivate them through satisfying their needs. |
|
6. |
Communication skills : A leader must be a good communicator. |
|
Communication – It is transfer of information from the sender to the receiver with the information being understood by the receiver. |
|
|
52 XII – Business Studies |
|
|
Elements of Communication Process – |
|
|
1. |
Sender – Who conveys his thoughts or ideas |
|
2. |
Message – Ideas, feelings, suggestions, order etc. |
|
3. |
Encoding – Converting the message into communication symbols such as words / pictures etc. |
|
4. |
Media – Path/ Channel through which encoded message is transmitted to receiver e.g., face to face, phone call, internet etc. |
|
5. |
Decoding – Converting encoded symbols of the sender. |
|
6. |
Receiver – Who receives communication of the sender. |
|
7. |
Feed back – All those action of receiver indicating that he has received and understood message of sender. |
|
8. |
Noise – Some obstruction or hindrance to communication like poor telephone connection, inattentive receiver. |
|
Importance of Communication 1. Facilitates Coordination – between interrelated departments and sections thus creating a unity of purpose and action. |
|
|
2. |
Provides data necessary for decision makings – When information is effectively and efficiently communicated to management. |
|
3. |
Increases Managerial Efficiency – By Conveying the goals, targets, instructions. |
|
4. |
Promotes cooperation and Industrial Peace – The two way communication promotes cooperation and mutual understanding between the management and workers. |
|
5. |
Establishes effective leadership – Effective communication helps to influence subordinates – while influencing leader should posses good communication skills. |
|
Formal Communication – refer to official communication which takes place following the chain of command. Classification of formal communication – |
|
|
1. |
Vertical communication – Flows vertically i.e., upwards or downwards through formal channels |
|
i) Downward Communication – Higher to lower level like plans, policies, rules etc. |
|
|
53 XII – Business Studies |
|
ii) Upward Communication – Subordinate to superior like suggestions, grievances, reports etc.
2. Horizontal / lateral Communication – between persons holding positions at the same level of ther organisation e.g., production manager may contact marketing manager about product design, quality etc.
Communication Net works of a Formal Communication.
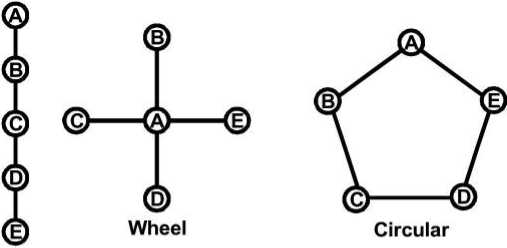
Single Chain
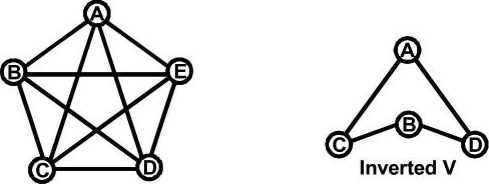
Free Flow
Informal Communication : Communication that takes place without following the formal lines of communication is said to be internal communication. There is no fixed direction or path for the flow of information.
Grapevine or Informal Communication Networks
- Single Strand – Each person communicates with the other in sequence.
- Gossip – Each person communicates with all on non-selective basis.
- Probability – The individual communicates randomly with other individual.
- Cluster – the individual communicates with only those people whom he trusts.
|
Difference between Formal & Informal Communication |
||
|
Basis Formal Communication |
Internal Communication |
|
|
1. |
Meaning within the official chain of command |
Between individuals and groups which are not officially recognised. |
|
2. |
Channel Through a definite path |
No definite path |
|
3. |
Speed Slow – because all information has to pass through an established chain of command |
Very fast – Cuts across all the official channels. |
|
4. |
Nature More rigid and cannot be modified |
Flexible and varies from individual to individual. |
|
5. |
Expression It is mostly expressed in written form. |
It mostly tends to be oral |
|
Barriers to Effective Communication – |
||
|
1. |
Semantic Barriers – Concerned with problems and obstructions in the process of encoding or decoding of message into words or impressions Semantic barriers are as follows. |
|
|
1. |
Badly expressed message |
|
|
2. |
Symbols with different meanings. |
|
|
3. |
Faulty Translations. |
|
|
4. |
Unclarified assumptions – Subject to different interpretations. |
|
|
5. |
Technical Targon – Technical words may not be understood by the workers. |
|
|
Psychological Barriers – The state of mind of both sender and receiver affect the process of communication. Psychological barriers are as follows. |
||
|
1 |
Premature Evaluation – Judgement before listening. |
|
|
2. |
Lack of attension. |
|
|
3. |
Loss by transmission and Poor Retention – When oral communication passes through various levels – destroy the structure of the message. |
|
|
4. |
Distrust – If the parties do not believe each other. |
|
|
55 |
XII – Business Studies |
|
Factor related to organisation structure.
- Organisational Policy
- Rules and regulations.
- Status.
- Complexity in organisation structure.
Personal Barriers – of superiors and subordinates
- Fear of challenge to authority.
- Lack of confidence of superior on his subordinates.
- Unwillingness to communicate.
- Lack of Proper incentives.
Improving Communication Effectiveness.
- Clarify the ideas before communication.
- Communicate according to the needs of receiver.
- Consult others before communicating.
- Be aware of language, tone and content of message.
- Ensure proper feedback.
- Follow up communication.
- Be a good listner.
- Which function of management is known as Management-in-action ?
- How supervision is helpful in maintaining discipline?
- What is Economic Safety?
- What is meant by Job Enrichment as a type of non-monetary incentives?
- What is meant by Leadership ?
- What is meant by Integrity ?
- A leader does not wait for opportunities but creates them . This statement is related to which quality of a good leader?
- What is meant by NOISE in communication process?
- What is meant by Feedback in communication process?
- What is meant by Grapevine ?
- Direction is the least important function of management . Do you agree with this statement? Give any two reasons in support of your answer.
- The post of supervisor should be abolished in the hierarchy of Managers . Do you agree? Give any three reasons in support of your answers.
- Explain how supervision facilities control?
- Motivation can be either positive or negative. How?
- Motivation helps to reduce absentism in the organisation. Clarify.
- Explain any four principles of directing.
- State any four characteristics of motivation.
- Clarify Job Enrichment and Job Securing as non-financial Motivators.
- Explain the importance of leadership as the directing functions of management.
- Explain any four factors which are likely to disrupt effective communication.
- Supervision is an important element of directing function . Explain any four reasons in support of the above statement.
- Explain different financial and non-financial incentives used to motivate employees of a company.
- Effectiveness of Leadership depends on the qualities of the leader . Explain any four such qualities of a leader.
- In an organization there are many leaders. But a good leader must be a distinguished one. Suggest any four qualities that a good leader must possess.
- Explain the meaning and importance of communication process.