UNIT 2
Concept of Principle of Management :
Principle of Management are the broad and general guidelines for managerial decision making. They are different from principles of science as they deal with human behaviour. They are different from techniques of management as techniques are method whereas principles are guidelines to action and decision making. Principle of management are different from values which are formed as generally accepted behaviour in society and having moral coordination where-as principles are formed through research having teachnical nature.
Nature of Principles of Management
The nature of principles of management can be described in the following points :
- Universal applicability i.e. they can be applied in all types of organizations, business as well as non-business, small as well as large.
- General Guidelines : They are General Guidelines to action which however do not provide readymade solutions as the business environment is very changing or dynamic.
- Formed by practice and experimentation : They are developed after thorough research work on the basis of experiences of managers.
- Flexible which can be modified by the practicing manager as per the demands of the situations.
- Mainly Behavioural : Since the principles aim at influencing human behaviour they are behavioural in nature.
- Cause and Effect relationship : They intend to establish relationship between cause & effect so that they can be used in similar situations.
- Contingent : Their applicability depends upon the prevailing situation at a particular point of time.
Significance of the Principles of Management
The significance of principles of management can be derived from their utility
which can be understood from the following points :
- Providing managers with useful insights into reality.
- Optimum utilization of resource and effective administration.
- Scientific decisions.
- Meeting the changing environmental requirements.
- Fulfilling social responsibility.
- Management training, education and research.
Taylor s Scientific Management :
F.W. Taylor (1856-1915) was an American mechanical engineer who believed
in analyzing the work scientifically and finds one best way to do any work.
His book Principles of Scientific Management was published in 1911.
Principles of Scientific Management :
Taylor gave the following principles of scientific management :
- Science and not the rule of thumb : which implies developing one standard method through work study unifying the best practices globally which would result in optimum resource utilization.
- Harmony, Not discord : which implies that there sould be mental revolution on part of managers, workers and owners to respect each other s role and eliminate any class conflict to realize organizational objectives.
- Cooperation not individualism : It is an extension of the Principle of Harmony, Not discord whereby constructive suggestions of workers should be adopted and they should not go on strike as both management and workers share responsibility and perform together. Infact there should be complete cooperation between the labour and the management instead of individualism.
- Development of Each and Every Person to His or Her greatest Efficiency and Prosperity : Which implies development of competencies of all persons of an organization after their scientific selection and assigning work suited to their temperament and abilities.
Techniques of Scientific Management
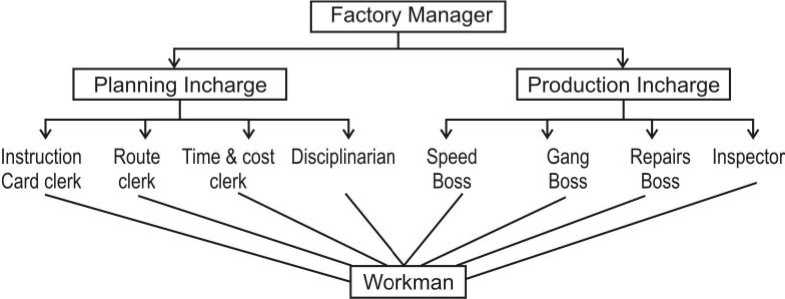
(1) Functional Foremanship : Functional foremanship is a technique in which planning and execution are saparated. There are 8 types of specialized professionals 4 each under planning and execution who keep a watch on all workders to extract optimum performance.
- Standardisation and Simplification of work : Standardization refers to developing standards for every business activity whereas Simplification refers to eliminating superfluous varieties of product or service. It results in savings of cost of labour, machines and tools. It leads to fuller utilization of equipment and increase in turnover.
- Method Study : The objective of method study is to final out one best way of doing the job to maximise efficiency in the use of materials, machinery, manpower and capital.
- Motion Study : Motion study seeks to eliminate unnecessary motions in the execution of a job to enable it to be completed in less time efficienty.
- Time study : It determines the standard time taken to perform a well defined job. The objective of time study is to determine the number of workers to be employed, frame suitable incentive schemes & determine labour costs.
- Fatigue study : Fatigue study seeks to determine amount and frequency or rest intervals in completing a task.
- Differential Piece Wage system : Differential Piece Wage system seeks to reward a more efficient worker by giving him/her more wages for more quantity of standard production achieved.
- Mental Revolution : It involves a change in the attitude of workers and management towards one another from competition to cooperation.
Foyol s Principles of Management : Henri Fayol (1841-1925) was a French
Mechanical engineer who gave 14 general principles of Management which are
as under :
- Division of Work : Work is divided into small tasks / jobs and each one is done by a trained specialist which leads to greater efficiency.
- Authority and Responsibility : Managers are empowered with authority to give orders and obtain obedience and responsible for the accomplishment of task for which they are granted authority.
- Discipline : it is the obedience to organizational rules and employment agreement which are necessary for working of the organization.
- Unity of Command : There sould be only one boss for every employee. If an employee gets orders from two superiors at the save time the principle of unity of command is voilated.
- Unity of Direction : Each group of activities having the same objective must have one head and one plan. This ensures unity of action and coordination.
- Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest : The Interest of an organization should take priority over the interests of any one individual employee.
- Remuneration of Employees : The overall pay and compensation should be fair to both employees and the organization.
- Centralization and Decentralization : The concentration of decision making authority is called centralization whereas its dispersal among more than one person is known as decentralization. Both should be balanced.
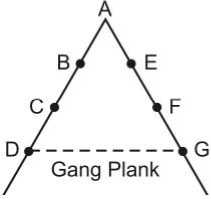
- Scalar Chain : The formal lines of authority between superiors and subordinates from the highest to the lowest ranks is known as scalar chain. This chain should not be voilated but in emergency employees at same level can contact through Gang Plank.
- Order : A place for everything (everyone) and everything (everyone) in its place. People & materials must be in suitable places at oppropriate time for maximum efficiency.
- Equity : The working environment of any organization should be free from all form of discrimination and the principles of Justice and fair play should be followed.
- Stability of Personnel : After being selected and appointed after due and rigorous procedure the selected person should be kept at the post for a minimum period decided to show result.
- Initiative : Workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for improvements. Initiative means taking the first step with self motivation It is thinking out and executing the plan.
- Espirit De Corps : Management should promote team spirit, unity and harmony among employees. Management should promote a team work.
Difference between unity of command and unity of direction
Basis
(2) Meaning
(2) Aim
Unity of Command
One subordinate should receive orders from & should be responsible to only one superior.
Prevents dual subordination
Unity of Direction
Each group of activities having save objectives must have one head and one plan
Prevents overlapping of activities
(3) Implications Affects an individual employee
Affects the entire organisation.
Fayol versus Taylor :
While the work of Taylor concerned shop floor, the work of Fayol concerned General Principles applicable to all types of situations.
1 Mark Questions (To be answered in 1 word or 1 sentence)
- The Principles of Management are different from those used in pure science”. Write anyone difference.
- Why is it said that the management principles are universal?
- Different techniques were developed by Taylor to facilitate the Principles
of Scientific Management. One of them was ‘Fatigue study’. What is the objective of this study?
- List any two principles of “Scientific Management” formulated by Taylor for managing an organization scientifically?
- What is meant by principles of management?
- State anyone principle of scientific management.
- State any one reason why Principles of Management are important.
- Give the meaning of mental revolution as suggested by Taylor.
- Explain the following principles of management:-
- Equity.
- Remuneration of Employees.
- In your school, you observe that books, are kept in office, chalks in the library and office records in the staffroom. How will that affect the achievement of school objectives? Which aspect of management is lacking and why? As a manager, what steps will you take to rectify the shortcomings?
5/6 Marks Question (to be answered in about 150 words)
- Explain any two techniques of Taylor s Scientific Management.
- Explain the following principles of Fayol with example.
- Unity of Command
- Unity of Direction
- Order
- Espirit De Corps.