NCERT Exemplar Problems Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 11 Three Dimensional Geometry
Short Answer Type Questions


5. Prove that the line through A(0, -1, -1) and B(4, 5, 1) intersects the line through C(3, 9,4) and D(- 4,4,4).
Sol. We know that, the equation of a line that passes through two points (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2) is

7. Find the equation of a plane which bisects perpendicularly the line joining the points A(2, 3,4) and 5(4, 5, 8) at right angles.

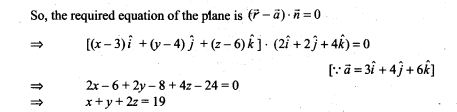
8. Find the equation of a plane which is at a distance 3 √3 units from origin and the normal to which is equally inclined to coordinate axis.
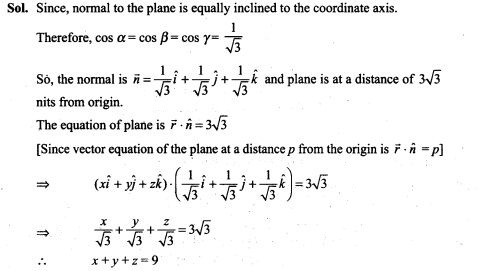
9. If the line drawn from the point (-2, -1,-3) meets a plane at right angle at the point (1, -3, 3), find the equation of the plane.
Sol. Since, the line drawn from the point B(-2, -1,-3) meets a plane a plane at right angle at the point 4(1,-3, 3).
So, the plane passes through the point 4(1, -3, 3)
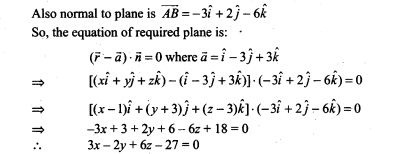
10. Find the equation of the plane through the points (2, 1, 0), (3, -2, -2) and (3, 1, 7).
Sol. We know that, the equation of a plane passing through three non-collinear points (x1. y1, z1), (x2, y2, z2) and (x3, y3, z3) is


14. O is the origin and A is (a, b, c). Find the direction cosines of the line OA and the equation of plane through A at right angle to OA.

Long Answer Type Questions


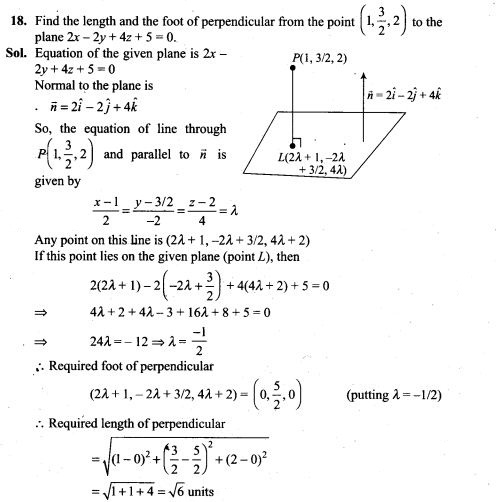
19. Find the equations of the line passing through the point (3,0,1) and parallel to the planes x + 2y = 0 and 3y-z = 0.


20. Find the equation of the plane through the points (2,1, -1) and (-1,3,4), and perpendicular to the plane x-2y + 4z = 10.

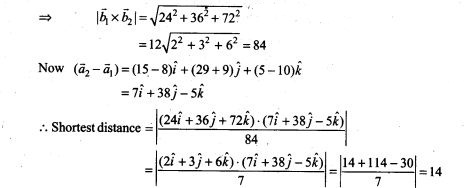
22. Find the equation of the plane which is perpendicular to the plane 5x + 3y + 6z + 8 = 0 and which contains the line of intersection of the planes x + 2y + 3z – 4 = 0 and 2x + y- z + 5 = 0.



27. Show that the straight lines whose direction cosines are given by 2l+2m -n=0 and mn + nl + lm = 0 are at right angles.
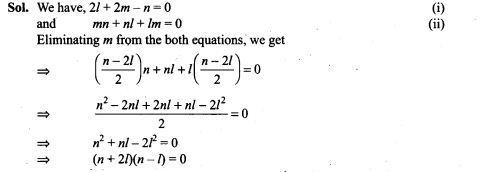

Objective Type Questions
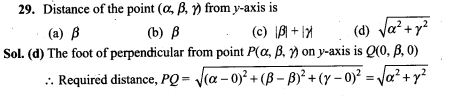
30. If the directions cosines of a line are k, k, ‘k, then

33. The reflection of the point (α, β,γ) in the xy-plane is
(a) (α, β,0) (b) (0,0, γ) (c) (-α, -β, γ) (d) (α, β,-γ)
Sol. (d) In xy-plane, the reflection of the point (α, β,γ) is (α, β,-γ)
34. The area of the quadrilateral ABCD, where A(0,4,1), B(2, 3, -1), C(4, 5, 0) and D(2, 6,2) is equal to
(a) 9 sq. units (b) 18 sq. units (c) 27 sq. units (d) 81 sq. units

35. The locus represented by xy + yz = 0 is
(a) A pair of perpendicular lines (b) A pair of parallel lines
(c) A pair of parallel planes (d) A pair of perpendicular planes
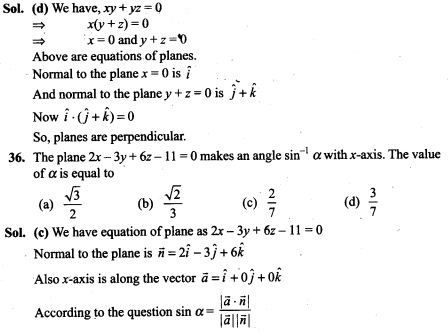
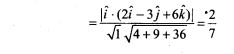
Fill in the Blanks Type Questions

True/False Type Questions



