LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (4 MARKS)
Q.1. Describe in brief the role of human resources in economic development.
Ans. Role of Human Resource.
(i) Higher Productivity. Investment in human capital yields a return just like investment in
physical capital. This can be seen directly in form of higher incomes earned because of
higher productivity of the more educated or the better trained persons as well as the higher
productivity of healthier people. India’s Green Revolution and IT Revolution are good
examples of human resources development.
(ii)Better Utilisation of Resources. Countries like Japan have invested in human resource.
They did not have any natural resource. They could become rich/developed because of
investments in people specially in the fields of education and health. These people have
made efficient use of other resources like land and capital. Efficient technology developed
by people have made these countries developed.
(iii)Source of Demand. Human beings make demand for the output of goods and services
produced in the country. Expansion of market for various types of foods and services
further leads to increase in production.
Q.2. Is it necessary to check population growth?
Ans.India has vast manpower. But she could not utilise this manpower for country’s economic
development. Rather, population growth has posed a big threat for the country. It needs to be
controlled without further delay. It has become a big hurdle in the way of country’s economic
development in the following ways :
(i) Despite considerable growth in national income, per capita income could not increase
much due to fast population growth.
(ii) Fast population growth is considered as one of the major causes of unemployment in
India.
(iii) Heavy pressure of population has led to the problem of overcrowding in cities, unplanned
urbanisation, emergence of slums etc.
All these factors lead us to believe that rapidly growing population has become a big
challenge before the Indian economy. It is the biggest roadblock in the path of its
economic development. Indian poverty is deeply rooted in population growth. It, therefore,
becomes highly necessary to check population growth in India.
Q.3. What are the strategies that the government has undertaken to reduce unemployment?
[CBSE 2010]
Ans. Strategies undertaken by the government to reduce unemployment.
(i) Rural Self-Employment Scheme : Our government has introduced various schemes for creating self-employment opportunities in rural areas. In April 1999, Swarna Jayanti
Gram-Sewa Rozgar Yojana (SGSY) was introduced whose main aim was to improve
opportunities of self-development in rural areas.
(ii)Wage-employment Schemes : Main objective of this scheme was to provide
opportunities for wage earning to rural people. Since June 23, 1999, all these schemes
were merged with Jawahar Gram Samridhi Yojana (JGSY).
(iii)Various schemes for providing employment to educated in urban areas : Various
schemes (like Prime Minister Rozgar Yojana PMRY), Swarn Jayanti Shahri Rozgar Yojana
(SJSRY) has been started by the government for providing employment to the educated
youth in urban area.
Q.4. What is an economic activity? What are various activities undertaken in the primary
sector, secondary sector and tertiary sector? [CBSE 2010]
Ans. Economic activities :All such activities which give us some income are called economic
activities. Pulling cycle-rickshaw, cleaning houses, selling vegetables and working in schools,
factories, banks etc. are economic activities.
Activities undertaken in Primary, Secondary and Tertiary sectors :
(i) Primary Sector : Activities concerned with collecting or making available material
provided by nature are included in primary sector like agriculture, poultry farming,
mining, fishing etc.
(ii)Secondary Sector : The activities which are associated with transforming raw material or
primary products into commodities useful to man such as manufacturing etc.
(iii)Tertiary Sector : The activities which are essential for running modern factories in a big
way are termed as tertiary sector. Activities like trading, banking, health, education,
insurance etc. are included in tertiary sector.
Q.5. Study the graph and answer the following questions : [CBSE 2010]
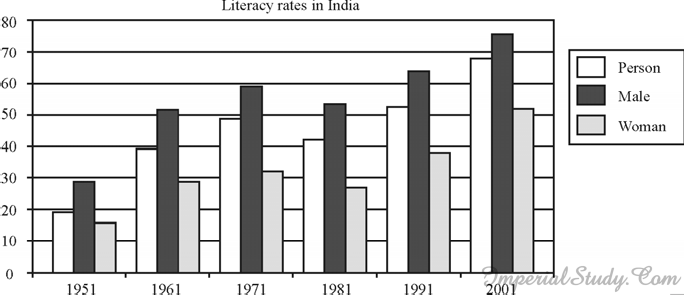 (a) By how much have literacy rates of the population gone up since 1951? 1
(a) By how much have literacy rates of the population gone up since 1951? 1
(b) Why is the literacy rate lower among women? 1
(c) Explain two measures introduced by the government to improve enrolment in elementary
education in the country. 2
Ans. (a) Literacy rate of population in 1951 was 19%, while in 2001 the rate shot up to 65%.
So there is an increase of 46% in 50 years.
(b) Literacy rate is low among women because of sex-discrimination. Females are not
provided equal opportunities of education in rural areas as of male members of family.
(c)Sarva Siksha Abhiyan : Main objective of this initiative introduced by Central
government was to provide elementary education to all children in the age group of 6-14
years by 2010.
Mid-day Meal Scheme : This scheme was introduced to encourage attendance and
retention of children and improve their nutritional status.
Q.6. Why did Japan emerge as a developed country inspite of its poor natural resource?
[2010 (T-1)]
Ans.Japan emerged as a developed country inspite of its poor natural resource because :
(i) as they did not have any other resource they invested in the development of human
resource and import other required resources.
(ii) they invested in better health and education facilities for people to make them efficient so
that they can efficiently use resources like land and capital.
(iii) efficiency and the technology evolved by the educated and literate people have made it
rich and developed.
(iv) they provide skill based education to the population so that they largely supported in the
national income.
Q.7. Discuss about the employment scenario in the three sectors in India. [2010 (T-1)]
Ans. Primary Sector :Agriculture is the most labour absorbing sector of the economy. In recent
years, there has been a decline in the dependence of population on agriculture partly because
of disguised unemployment. Some of the surplus is moving from primary to secondary or
tertiary sectors.
Secondary Sector : Small scale manufacturing units absorb most of the labour in secondary
sector.
Tertiary Sector : Various new services have started employing labour in tertiary sector like
biotechnology, information technology and so on.
Q.8. “In the past and present migration of the people from rural to urban areas has shown
an upward trend.” What factors compel the rural people to migrate to cities?
[2010 (T-1)]
Ans.People have started moving from rural to urban areas because of the following factors :
(i)Education facilities : Urban areas have more organised and better quality education
facilities opportunities vocational education and education in specialised areas has
increased in urban areas. In urban areas focus is on increasing access, quality,
vocationalisation and networking on the use of information technology.
(ii)Health facilities : Availability of better hospitals and medical facilities make people move
from rural to urban areas. States like Bihar and Uttar Pradesh has poor health indices.
Therefore, in search of proper medical assistance people often move from rural to urban
sectors.
(iii)Employment facilities : Disguised unemployment in primary sector and rise of
employment opportunities in secondary and tertiary sector has given rise to migration of
people from rural areas to urban areas. In order to increase the income of family, people
move from one occupation to another and one area to another.
Q.9. How does Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan help in improving elementary education in India?
[2010 (T-1)]
Ans.‘Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan’ aims at providing elementary education to all children in the age group
of 6-14 years of age by the year 2010. It is the initiative of central government in partnership
with the states, the local government and the community for achieving the goal of
universalisation of elementary education.
As a result of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan there has been a significant growth in literacy rate from
18% in 1951 to 65% in 2001. The primary school system has expanded to over 5,00,000
villages in India. Mid day meal scheme has also started by government to ensure attendence
and improve nutritional states of the children. Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan has added to the literate
population of India.
Q.10. Explain some strategies made by Government to solve the problem of unemployment in
India. [2010 (T-1)]
Ans.(i) Opening schools in villages : Opening vocational and elementary schools in villages
create employment opportunities for people living these. Earlier people were involved in
primary sector only but now they have better employment opportunities in other sectors
also.
(ii)Small scale manufacturing : Opening opportunities of self-employment in the form of
small scale manufacturing units like basket weaving etc adds to the employment
opportunities in removes disguised and seasonal unemployment away people.
(iii)Introduction to modern farming methods : Use of modern farming methods gave the
surplus members of family to get involved in other employment opportunities.
(iv)Proper health facilities : Improvement in health facilities in urban and rural areas
improved in quality of human resource which in turn work more efficiently and
contributed to national income.
Q.11. How the investment in Human Capital can be of immense importance for a society as a
whole? State any four advantages. [2010 (T-1)]
Ans.Human Capital can be defined as the knowledge, ability, skill and physical capactity of the
people which help them to produce more.
Human beings can be turned into resources only if their qualitative aspects are developed.
Education and health are the major human resource inputs of a country. Human capital is
beneficial both individually as well as socially.
(i) Human capital contributes to the social development of the country.
(ii) Human capital contributes to the economic development of the country.
(iii) Human capital helps in proper utilisation of resources available or imported in the country.
(iv) Human capital also contributes in the race of development from an underdeveloped to a
developed nation.
Q.12. Explain difference between vicious and virtuous cycle of life with reference to human
resource. [2010 (T-1)]
Ans.Quality of present human resource affects the quality of human resource for the coming
generation. For example, educated parents are found to invest more heavily on the education,
health and nutrition of their child. They are more conscious about the qualtiy upbringing of
their child. Thus, they create a virtuous cycle of life.
On the other hand, uneducated parents who are themselves lacking in education, health,
nutrition and hygiene and are not conscious of the importance of these in the lives of their
children. They are unable to provide quality upbringing of their children. Thus, they create a
vicious cycle of life.