Financial Statement I (Without Adjustments)
- Meaning
Financial statements are the final products of an accounting process which begins with the identification of accounting information and recording it in the books of primary entry. Financial statements are prepared by following the accounting concepts and conventions. These are the statements prepared at the end of accounting period and give information about the financial position and preformed of an enterprise.
A complete set of financial statements include
- Balance sheet (or position statement) which shows the financial position of an enterprise at a particular point of time.
- Trading and profit and loss account (or income statement) which shows the financial performance of business operations during an accounting period.
- Schedules and notes to accounts forming a part of balance sheet and profit and loss account.
Objectives and Importance of Financial Statement
The basic objectives of preparing financial statements are
- To present a true and fair view of the financial performance of the business.
- To present a true and fair view of the financial position of the business.
Various other objectives and importance of financial statements are as follows:
- Helps in determination of gross profit/gross loss
- Helps in determination of net profit/ net loss
- Comparison with the previous years
- Calculation of rations
- Maintaining provisions and reserves
Users of Financial Statements
Internal Users
- Owners
- Management
- Employees and workers
External Users
- Creditors
- Investors
- Banks and financial institutions
- Government its authorities
- Other parties
- Researchers
Income Statement
Income statement is prepared at the close of the year discloses the manner in the amount of profit and loss is arrived at, Income statement is divided in trading account and profit and loss account.
- Trading Account
Trading account is the first stage is the preparation of the final accounts. The trading account ascertains the rest from basic operational activities of the business.
Trading account is prepared to know the gross profit earned or gross loss incurred during the accounting period. Entries or items of debit side are opening side, purchases and other direct expenses and on credit side sales and closing stock are recorded.
The excess of sales over purchases and direct expenses is called gross profit, if the amount of purchase including direct expenses is more than the sales revenue, the resultant figure is gross loss.
The computation of gross profit can be shown in the form of equation as
Gross Profit = Net Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
Where, Net Sales = Total Sales – Sales Return
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Net Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
Net Purchases = Total Purchases – Purchases Return
- Format of Trading Account
Profit and Loss Account
For the year ended..
Dr Cr 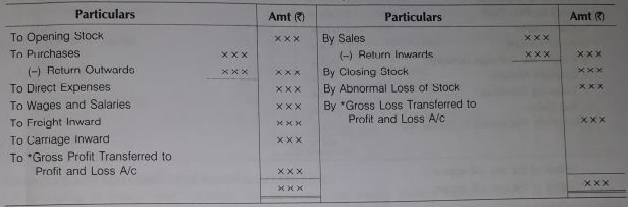
- Either gross profit or gross loss shall appear.
- Profit and Loss Account
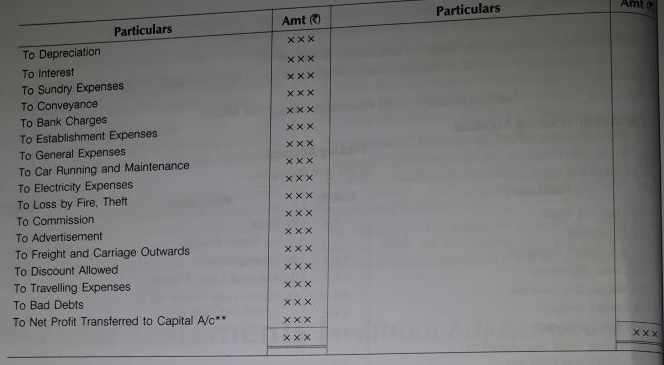
Profit and loss account is prepared after the preparation of trading account. It shows the financial performance of a business during an accounting period. It prepared to as certain the net profit earned or net loss incurred by the business entity during an accounting period.
Balance of trading account (gross profit or gross loss) is transferred to profit and loss account. The indirect expenses are transferred to the debit side of the profit and loss account. All revenues/gains other than sales are transferred to the credit side of the profit and loss account.
It the total of the credit side of the profit and loss account is more than the total of the debit side, the difference is the new profit for the period, of which is being prepared.
On the other hand, if the total of the debit side is more than the total of the credit side, the difference is the net loss incurred by the business firm.
In an equation form, it is shown as follows:
Net Profit = Gross Profit + Other Incomes – Indirect Expenses
- Format of Profit and Loss Account
Profit and Loss Account
For the year ended..

- Either of the two will appear.
- Either of the two will appear.
Operating Profit and Net Profit
- Operating Profit it is the profit earned through normal operations and activities of the business. Operating profit arises as a result of carrying out operating activities. Operating activities are the principle revenue producing activities of the enterprise and are those activities that are not investing or financing activities, means the excess of operating revenue over operating expenses or it is the excess of gross profit own operating expenses. It is also known as Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT).
It is calculated as
Operating Profit = Net Sales – Operating Cost
Or
= Net Sales – (Cost of goods sold + Administration and office expenses + Selling and distribution expenses)
Or
= Net Profit + Non-Operating Expenses – Non-Operating Income
Operating expenses include office and administrative expenses, selling and distribution expenses, case discount allowed, interest on bill payable and other short-term debts, bad debts and so on.
Net Profit = Sales (Cash and Credit) – Sales Return
- Net Profit means the excess of revenue (operating or non-operating) over expenses and losses (operating and non-operating). In other words, net profit is arrived at by deducting non-operating expenses and adding non- operating incomes form and in operating profit.
Non- Operating expenses are expenses which are incidental or indirect to the main operations of the business, they include interest on loan, charities and donations, loss on sale of fixed assets, extraordinary losses due theft, loss by fire and so on
Non- Operating incomes includes receipt of interest, rent, dividend, profit on sale of fixed assets etc.
Also Check out: TS Grewal Solutions for Adjustments in Preparation of Financial Statements Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 18
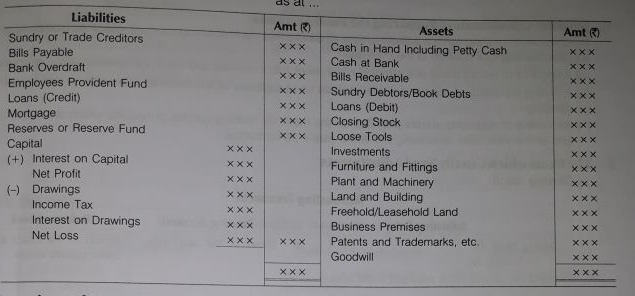
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a statement prepared for showing the financial position of the business summarizing the assets and liabilities at a given date. It is prepared at the end of the accounting period after the trading and profit and loss account have been prepared.
The assets reflect debit balances and liabilities (including capital) reflect credit balances.
It is called a balance sheet because it is a statement of balances of ledger accounts.
- Format of Balance Sheet
Balance Sheet
As at..
Grouping and Marshalling of Assets and Liabilities
- Grouping of assets and liabilities the term grouping means putting together items of similar nature under a common heading. The various item appearing in the balance sheet can also be properly grouped, e.g. the balance of accounts of cash, bank, debtors etc. can be grouped and shown under the heading of ‘current assets’.
- Marshalling of assets and liabilities Marshalling refers to the arrangement of assets and liabilities in a particular order. In a balance sheet the assets and liabilities are arranges either in the order of liquidity or permanence.
- Order of performance In case of performance, the most permanent assets or liabilities are out on the top in a balance sheet and thereafter they are arranged in their reducing level of permanence.
In other words, in case of assets, the ones which are to be used permanently in the business and are not meant to be sold are written first, e.g. goodwill and the ones which are most liquid are written last, e.g. cash in hand.
In case of liabilities, the payments to be made which are least urgent are written first, e.g. capital and the payments to be made which are most urgent are written last, e.g. short-term liabilities say short-term creditors (i.e. firstly capital, then long-term liabilities and at last short-term liabilities).
- Order of Liquidity ‘liquidity’ means the facility with which the assets may be converted into cash. In case of liquidity, the order is reversed.
In case of assets, the most liquid assets are written first, e.g. cash is hand and the least liquid assets are written last, e.g. goodwill.
In case of liabilities, the most urgent payments to be made are written first, e.g. short-term creditors and the least urgent payments to be made are written last, e.g. capital (i.e. firstly short-term liabilities, then long-term liabilities and in last capital).
It can be better understood with the general format of balance sheet in order of liquidity.
Methods of Preparation of Financial Statements
The financial statements, i.e. trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet can be presented in two ways:
- Horizontal from Under this form of presentation, the items are presented in ‘T’ shape, i.e. the items are shown side by side in trading and profit and loss account and also in the balance sheet. This form of preparing financial statements has been already discussed in the chapter.
- Vertical form Under vertical presentation, the final accounts are prepared in a form of statement, i.e. the items are presented in a single column with different items being shown one below the other in purposeful sequence.